Is it normal for pregnant women to get diabetes?
Pregnancy brings many physical and hormonal changes, and along with excitement and anticipation, it often raises health-related questions. One common concern among expectant mothers is whether developing diabetes during pregnancy is normal. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy is important, as early awareness helps ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the baby.
Many women are surprised when they hear about pregnancy-related diabetes, especially if they have never had blood sugar issues before. This leads to a frequently asked question: can pregnancy cause diabetes? The answer is yes—in some cases. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect how the body uses insulin, leading to a condition known as gestational diabetes. While it may sound alarming, it is more common than many people realize and can usually be managed effectively with proper medical care.
One reason this condition often goes unnoticed is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms can be mild or even absent in the early stages. Some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, or blurred vision, but these symptoms can also overlap with normal pregnancy changes. This makes regular monitoring of blood sugar in pregnancy especially important.
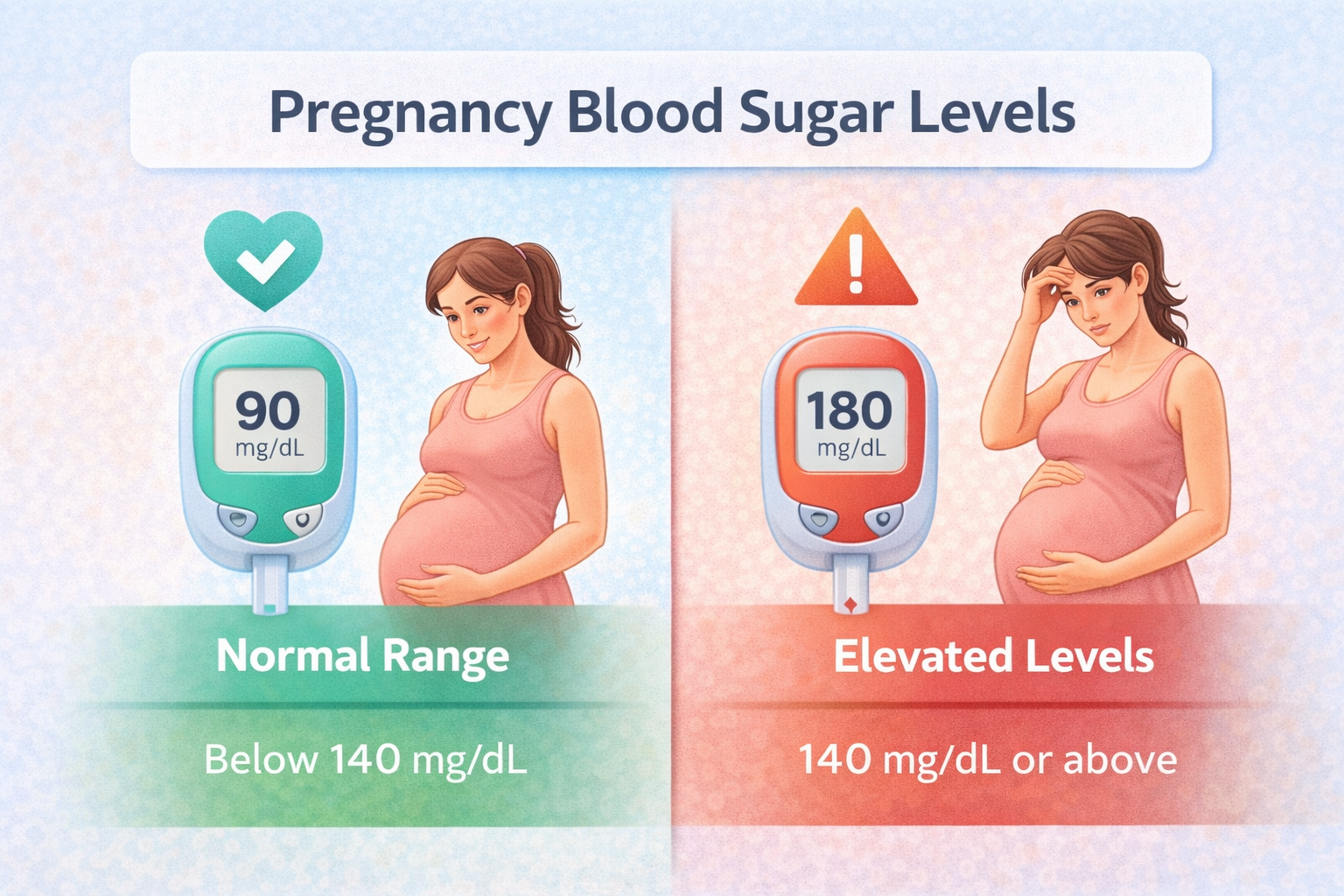
Doctors closely monitor glucose levels to ensure they remain within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. When blood sugar rises above this range, it can increase the risk of complications such as excessive birth weight, early delivery, or delivery-related challenges. Early detection allows doctors to guide mothers on diet, activity, and—if necessary—medication to maintain healthy glucose levels.
Routine screening plays a crucial role in identifying diabetes during pregnancy. Many women search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me as part of their prenatal care. These tests are typically done between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy, though high-risk women may be tested earlier. Regular testing ensures timely diagnosis and helps prevent complications.
Choosing the right medical support is equally important. Consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures personalized care, proper monitoring, and expert guidance throughout pregnancy. With the right medical team, most women with diabetes in pregnancy go on to have healthy pregnancies and deliveries.

It’s also important to remember that developing diabetes during pregnancy does not mean you will have diabetes for life. In many cases, blood sugar levels return to normal after delivery. However, women who experience diabetes in pregnancy may have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later, making postpartum follow-up equally important.
While not every pregnant woman develops diabetes, it is a common and manageable condition. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, and staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range are key steps toward a healthy pregnancy. With timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me and guidance from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, expectant mothers can approach pregnancy with confidence and peace of mind.
What Is Diabetes During Pregnancy?
Diabetes during pregnancy is a condition in which a woman’s blood sugar levels become higher than normal while she is expecting. This condition is medically referred to as gestational diabetes and is a common form of diabetes in pregnancy. It usually develops in the second or third trimester and affects women who may not have had any blood sugar issues before becoming pregnant.
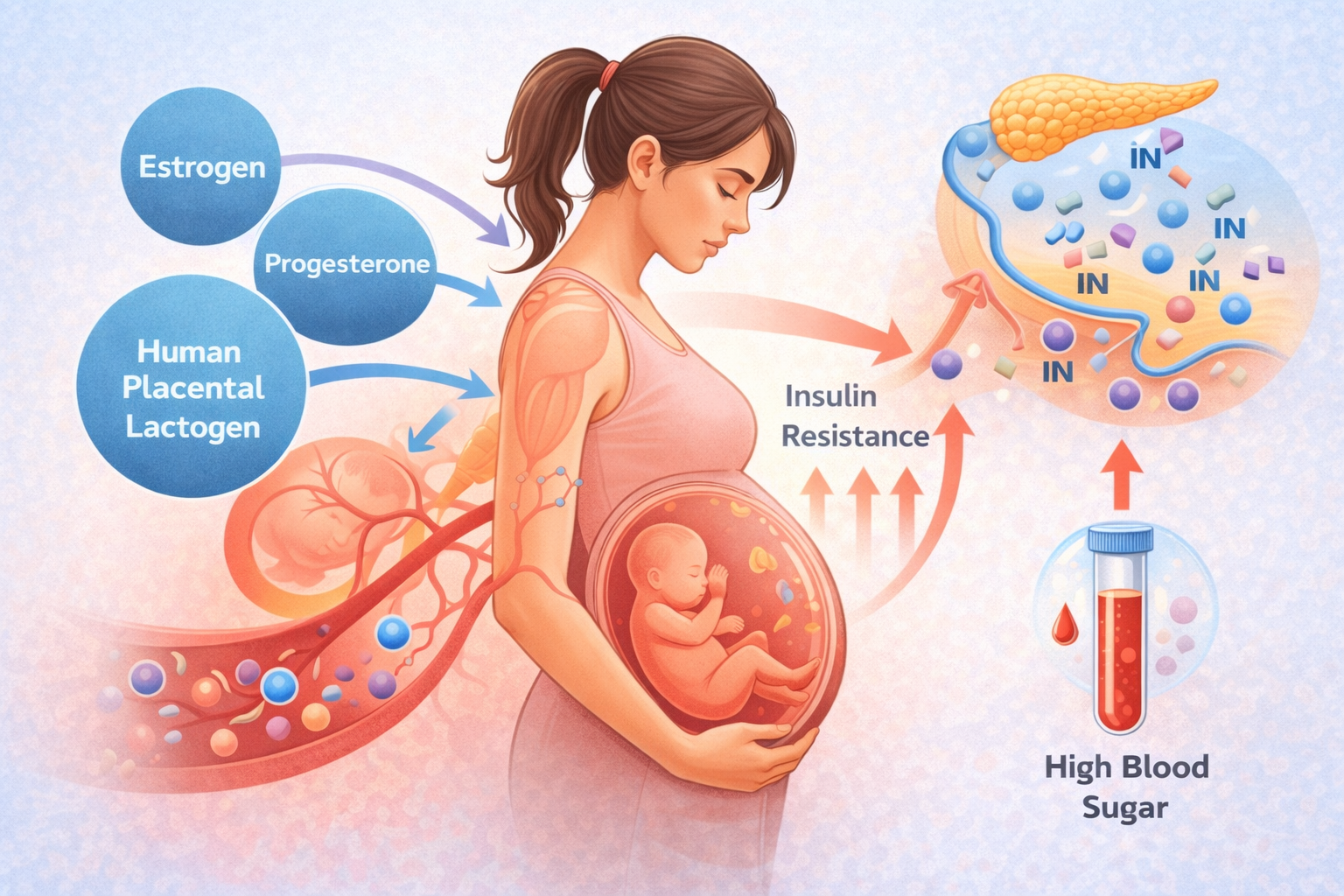
Many expectant mothers wonder, can pregnancy cause diabetes? The answer lies in the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. The placenta produces hormones that help the baby grow, but these hormones can also interfere with how insulin works in the mother’s body. When insulin becomes less effective, blood sugar levels rise, leading to diabetes during pregnancy.
One challenge with diabetes during pregnancy is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often mild or mistaken for normal pregnancy discomforts. Some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, tiredness, or blurred vision, but many feel no noticeable symptoms at all. This is why routine screening and regular monitoring of blood sugar in pregnancy are so important.
Doctors closely track glucose levels to ensure they stay within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. When blood sugar levels rise above this range, it can increase health risks for both the mother and the baby. Elevated sugar levels may lead to excessive fetal growth, delivery complications, or a higher chance of cesarean birth if not properly managed.
Screening for diabetes during pregnancy is a standard part of prenatal care. Many women search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to understand where and when testing will be done. These tests are usually performed between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy, though women with higher risk factors—such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or previous gestational diabetes—may be tested earlier.
Once diagnosed, working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy becomes essential. A specialist helps guide mothers through blood sugar monitoring, meal planning, physical activity, and medication if required. With proper medical care, most women with diabetes in pregnancy can maintain healthy glucose levels and deliver healthy babies.
It is also important to understand that diabetes during pregnancy is usually temporary. In most cases, blood sugar levels return to normal after childbirth. However, women who experience gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, making post-pregnancy follow-up equally important.
Diabetes during pregnancy is a common and manageable condition caused by hormonal changes that affect insulin function. Recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, and undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me are key steps toward a healthy pregnancy. With guidance from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, women can confidently manage diabetes in pregnancy and protect both their own health and their baby’s well-being.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy in women who did not previously have blood sugar problems. It is one of the most common forms of diabetes in pregnancy and usually appears in the second or third trimester. Although hearing the word “diabetes” can be alarming, gestational diabetes is a manageable condition when detected early and treated correctly.
Many women wonder, can pregnancy cause diabetes? During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that support the baby’s growth. However, these hormones can reduce the effectiveness of insulin, the hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar. When the body cannot produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance, blood sugar in pregnancy begins to rise, leading to gestational diabetes.
One reason gestational diabetes can be challenging to identify is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often mild or unnoticeable. Some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, or blurred vision, but these symptoms can easily be mistaken for normal pregnancy changes. Because symptoms are unreliable, routine testing becomes essential for early detection.
Monitoring glucose levels helps ensure they remain within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. When blood sugar levels are consistently higher than normal, it can affect both the mother and the baby. Poorly controlled gestational diabetes may increase the risk of excessive birth weight, early delivery, or complications during labor. This makes timely diagnosis and proper management crucial.
Most pregnant women undergo screening tests between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Many expectant mothers search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to understand where they can get tested conveniently. These tests are simple, safe, and play a key role in protecting maternal and fetal health. Women with higher risk factors—such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or previous gestational diabetes—may be tested earlier.
Once diagnosed, care from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy is highly recommended. A specialist helps create a personalized care plan that may include dietary changes, regular blood sugar monitoring, safe physical activity, and medication or insulin if needed. With expert guidance, most women can keep their blood sugar levels well controlled throughout pregnancy.
An important aspect of gestational diabetes is that it is usually temporary. In many cases, blood sugar levels return to normal after childbirth. However, women who experience diabetes in pregnancy have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This makes postpartum follow-up and long-term lifestyle management important.
Why Does Diabetes Occur During Pregnancy?
Many expectant mothers are surprised when they are diagnosed with diabetes during pregnancy, especially if they have never had blood sugar issues before. This leads to a common question: can pregnancy cause diabetes? The answer lies in the complex hormonal and metabolic changes that occur to support the growing baby. Understanding why diabetes in pregnancy occurs helps reduce fear and encourages early management.
During pregnancy, the placenta releases several hormones that help the baby grow and develop. However, these hormones can interfere with how insulin works in the mother’s body. Insulin is responsible for regulating blood sugar in pregnancy by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. When pregnancy hormones reduce insulin sensitivity, glucose remains in the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
As pregnancy progresses, the body naturally becomes more insulin-resistant, particularly in the second and third trimesters. In most women, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. However, in some cases, insulin production is not sufficient, and blood sugar levels rise above the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, leading to gestational diabetes.
Genetics and lifestyle also play an important role in the development of diabetes during pregnancy. Women with a family history of diabetes, previous gestational diabetes, obesity, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a higher risk. Age can also be a factor, as women over 30 are more likely to experience insulin resistance during pregnancy.
One challenge is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often mild or mistaken for normal pregnancy changes. Increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue may not immediately raise concern, which is why routine screening is essential. Regular testing ensures that elevated blood sugar levels are detected early, even in women who feel perfectly healthy.
Doctors recommend routine screening between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Many women look for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule timely testing as part of prenatal care. These tests help identify glucose intolerance before it causes complications for the mother or baby.
Once diabetes in pregnancy is diagnosed, working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy becomes crucial. A specialist helps monitor blood sugar levels, suggests dietary changes, recommends safe physical activity, and prescribes medication or insulin if needed. Proper management significantly reduces the risk of complications.
It’s important to note that diabetes during pregnancy is usually temporary. In most cases, blood sugar levels return to normal after delivery. However, women who develop gestational diabetes have a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, making postpartum monitoring essential.
Diabetes during pregnancy occurs due to hormonal changes that reduce insulin effectiveness, combined with genetic and lifestyle factors. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, and undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me are key steps to a healthy pregnancy. With guidance from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, expectant mothers can manage this condition effectively and ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
How Common Is Gestational Diabetes in Pregnant Women?
Gestational diabetes is more common than many expectant mothers realize. While pregnancy is often associated with joy and anticipation, it also brings metabolic changes that can affect blood sugar in pregnancy. This leads many women to ask an important question: can pregnancy cause diabetes? The answer is yes—and it happens more frequently than most people expect.
Globally, gestational diabetes affects approximately 5% to 15% of pregnancies, with the rate varying based on ethnicity, lifestyle, age, and genetic factors. In countries like India, the numbers are often higher due to increasing rates of insulin resistance and lifestyle-related risk factors. This makes diabetes in pregnancy a growing public health concern rather than a rare complication.
One reason gestational diabetes is so widespread is that pregnancy naturally increases insulin resistance. Hormones released by the placenta interfere with insulin action, raising blood sugar in pregnancy. While many women compensate by producing more insulin, others cannot keep up with the demand, causing sugar levels to rise beyond the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
Despite its prevalence, gestational diabetes often goes unnoticed because pregnancy diabetes symptoms are usually mild or absent. Some women may feel excessive thirst, fatigue, or frequent urination, but these symptoms are often mistaken for normal pregnancy discomforts. As a result, many women are diagnosed only through routine screening.
Because of this, doctors strongly recommend regular screening tests for all pregnant women. Many expectant mothers search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to find reliable diagnostic centers. These tests are typically done between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy, though women with higher risk factors may be tested earlier.
Certain groups of women are more likely to develop gestational diabetes. These include women over the age of 30, those who are overweight, women with a family history of diabetes, and those who have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy. However, it’s important to note that gestational diabetes can also occur in women with no obvious risk factors, which is why universal screening is essential.
Once diagnosed, proper medical care significantly reduces risks. Consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures that blood sugar levels are monitored closely and managed effectively. With the right guidance, most women are able to keep their glucose levels within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range through diet, lifestyle changes, and medication if needed.
The good news is that gestational diabetes is usually temporary. In most cases, blood sugar in pregnancy returns to normal after delivery. However, women who develop diabetes during pregnancy have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, making follow-up testing and long-term lifestyle care important.
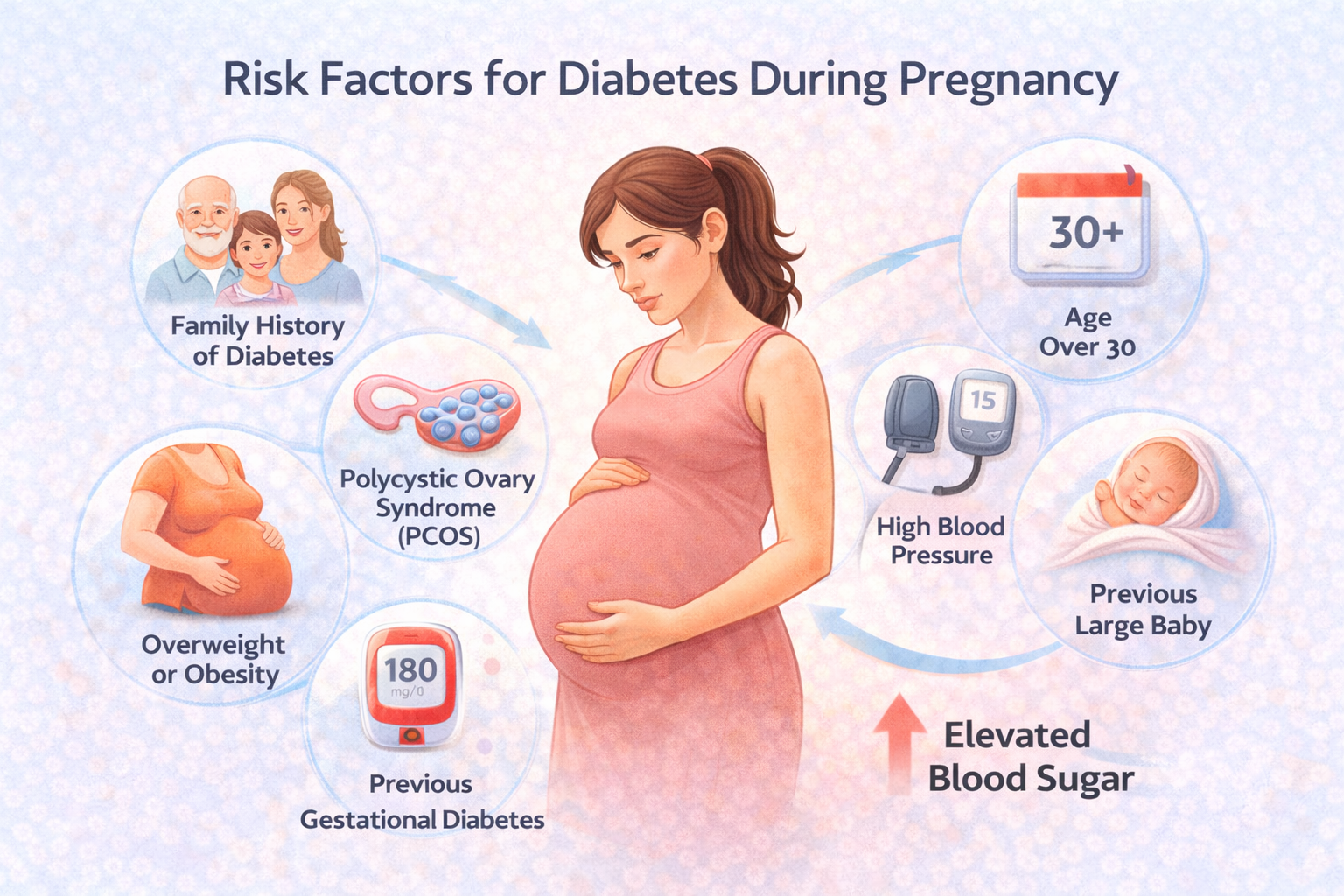
Risk Factors for Diabetes During Pregnancy
Understanding the risk factors for diabetes during pregnancy helps expectant mothers recognize why some women develop high blood sugar levels while others do not. Although many women ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes?, the truth is that pregnancy itself creates conditions that can raise blood sugar—but certain factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetes in pregnancy.
One of the most significant risk factors is insulin resistance, which naturally increases during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Pregnancy hormones can block the action of insulin, causing blood sugar in pregnancy to rise. When the body cannot produce enough insulin to compensate, blood sugar levels exceed the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, leading to gestational diabetes.
Age is another important factor. Women over the age of 30 have a higher risk of developing diabetes during pregnancy. As women age, insulin sensitivity tends to decrease, making it harder for the body to regulate glucose effectively during pregnancy.
Family history also plays a major role. Women with close relatives who have type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop diabetes in pregnancy. Genetics can influence how the body responds to insulin, increasing susceptibility even if the woman maintains a healthy lifestyle.
Body weight before pregnancy is another key factor. Women who are overweight or obese before conception have a higher risk of developing elevated blood sugar in pregnancy. Excess body fat increases insulin resistance, making it more difficult to maintain glucose levels within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
A previous history of gestational diabetes significantly raises the risk in future pregnancies. Women who experienced high blood sugar levels in an earlier pregnancy are more likely to develop the condition again. Additionally, women who previously delivered a baby weighing more than 4 kg may also be at increased risk.
Certain medical conditions can further increase risk. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), high blood pressure, and hormonal disorders are known to affect insulin sensitivity. Women with these conditions should be closely monitored throughout pregnancy.
Despite these risk factors, many women develop gestational diabetes without noticeable pregnancy diabetes symptoms. This is why routine screening is critical. Most pregnant women undergo glucose testing between 24 and 28 weeks, and many search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me as part of their prenatal care. Early detection allows timely intervention and better outcomes.
Once diagnosed, working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures personalized care. Specialists guide patients through blood sugar monitoring, diet planning, physical activity, and medication if required. With proper care, most women successfully maintain healthy glucose levels throughout pregnancy.
Risk factors for diabetes during pregnancy include hormonal changes, age, family history, weight, prior gestational diabetes, and certain medical conditions. While can pregnancy cause diabetes is a valid question, understanding individual risk factors helps women take proactive steps. Regular testing, awareness of pregnancy diabetes symptoms, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, and timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me—along with care from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy—can help ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy for both mother and baby.
Symptoms of Diabetes in Pregnant Women
One of the reasons diabetes during pregnancy often goes unnoticed is that its symptoms can be subtle or easily mistaken for normal pregnancy changes. Understanding the pregnancy diabetes symptoms is important so expectant mothers can seek timely testing and care. While not every woman experiences clear signs, being aware of possible symptoms helps ensure early detection of diabetes in pregnancy.
Many women ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes? Pregnancy-related hormonal changes can reduce insulin effectiveness, leading to increased blood sugar in pregnancy. When blood sugar rises beyond the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, certain symptoms may start to appear.

One of the most common symptoms is increased thirst. High blood sugar causes the body to pull fluids from tissues, making pregnant women feel unusually thirsty even when drinking enough water. Along with this, frequent urination may occur as the kidneys work harder to remove excess glucose from the blood. While frequent urination is common in pregnancy, an unusual increase can be a warning sign.
Another symptom is persistent fatigue. Pregnancy naturally causes tiredness, but diabetes-related fatigue tends to feel more intense and persistent. Elevated blood sugar in pregnancy prevents glucose from entering cells efficiently, reducing energy levels and causing ongoing exhaustion.
Some women may experience blurred vision, which occurs when high blood sugar affects fluid levels in the eyes. This symptom may come and go and is often overlooked unless blood sugar levels remain consistently high.
Unexpected weight gain or difficulty maintaining healthy weight patterns may also be linked to gestational diabetes. Additionally, some women experience recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections or yeast infections, as high sugar levels create a favorable environment for bacteria and fungi.
Despite these possible symptoms, many women with diabetes in pregnancy feel completely normal. This is why routine screening is essential. Doctors monitor glucose levels to ensure they remain within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, even when no symptoms are present.
Most pregnant women undergo screening between 24 and 28 weeks, and many search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule their tests conveniently. These tests help identify gestational diabetes early, allowing timely intervention and reducing the risk of complications.
Once symptoms or elevated blood sugar levels are detected, consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy becomes crucial. A specialist helps confirm the diagnosis, monitors glucose trends, and recommends lifestyle changes or medication if needed. With proper guidance, most women can keep blood sugar levels under control and continue a healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy diabetes symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and recurrent infections—but many women experience no symptoms at all. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, and undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me are essential steps for early diagnosis. With support from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, gestational diabetes can be managed effectively, ensuring the health and safety of both mother and baby.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is usually diagnosed through routine screening tests during pregnancy, often before any noticeable symptoms appear. Since many women wonder, can pregnancy cause diabetes?, understanding the diagnostic process helps reduce anxiety and highlights the importance of regular prenatal care. Early diagnosis of diabetes in pregnancy allows timely management and greatly reduces health risks for both mother and baby.
One of the challenges with gestational diabetes is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often mild or completely absent. Some women may feel increased thirst or fatigue, but these signs are commonly mistaken for normal pregnancy changes. Because symptoms are unreliable, doctors rely on standardized blood tests to monitor blood sugar in pregnancy accurately.
The most common screening method is the glucose challenge test (GCT). This test is typically performed between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. During the test, the pregnant woman drinks a sugary solution, and her blood sugar level is measured after one hour. This test does not require fasting and helps identify whether blood sugar levels are higher than the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
If the initial screening result is elevated, doctors recommend a follow-up diagnostic test called the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). This is a fasting test and provides a more detailed assessment. Blood sugar levels are measured at multiple intervals after consuming a glucose drink to determine how well the body processes sugar. This test confirms whether gestational diabetes is present.

Many expectant mothers search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule these screenings at reliable diagnostic centers. These tests are widely available and are a standard part of prenatal checkups. Women with higher risk factors—such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or previous gestational diabetes—may be tested earlier in pregnancy.
Once test results indicate elevated glucose levels, doctors compare them against established guidelines to determine whether blood sugar in pregnancy is within the normal range or requires medical attention. At this stage, consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy becomes essential. A specialist helps confirm the diagnosis, explains the results, and outlines a care plan tailored to the mother’s needs.
Diagnosis does not mean something has gone wrong—it simply means the condition has been identified early. With proper guidance, most women can manage gestational diabetes successfully through diet changes, regular monitoring, physical activity, and medication if required.
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through routine glucose screening tests that measure how the body handles sugar during pregnancy. Because pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often unclear, testing plays a crucial role in detecting diabetes in pregnancy early. By monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, expectant mothers can ensure a healthy pregnancy and safe delivery.
Can Gestational Diabetes Affect the Baby?
When a pregnant woman is diagnosed with gestational diabetes, one of the first concerns is how it may affect the baby. Since diabetes in pregnancy directly influences how nutrients reach the developing fetus, maintaining healthy glucose levels is essential. While gestational diabetes is manageable, uncontrolled blood sugar in pregnancy can increase certain risks for the baby.
Many expectant mothers wonder, can pregnancy cause diabetes? Hormonal changes during pregnancy can reduce insulin effectiveness, leading to higher blood sugar levels. When maternal blood sugar rises beyond the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, excess glucose crosses the placenta and reaches the baby. In response, the baby’s body produces more insulin, which can affect growth and development.
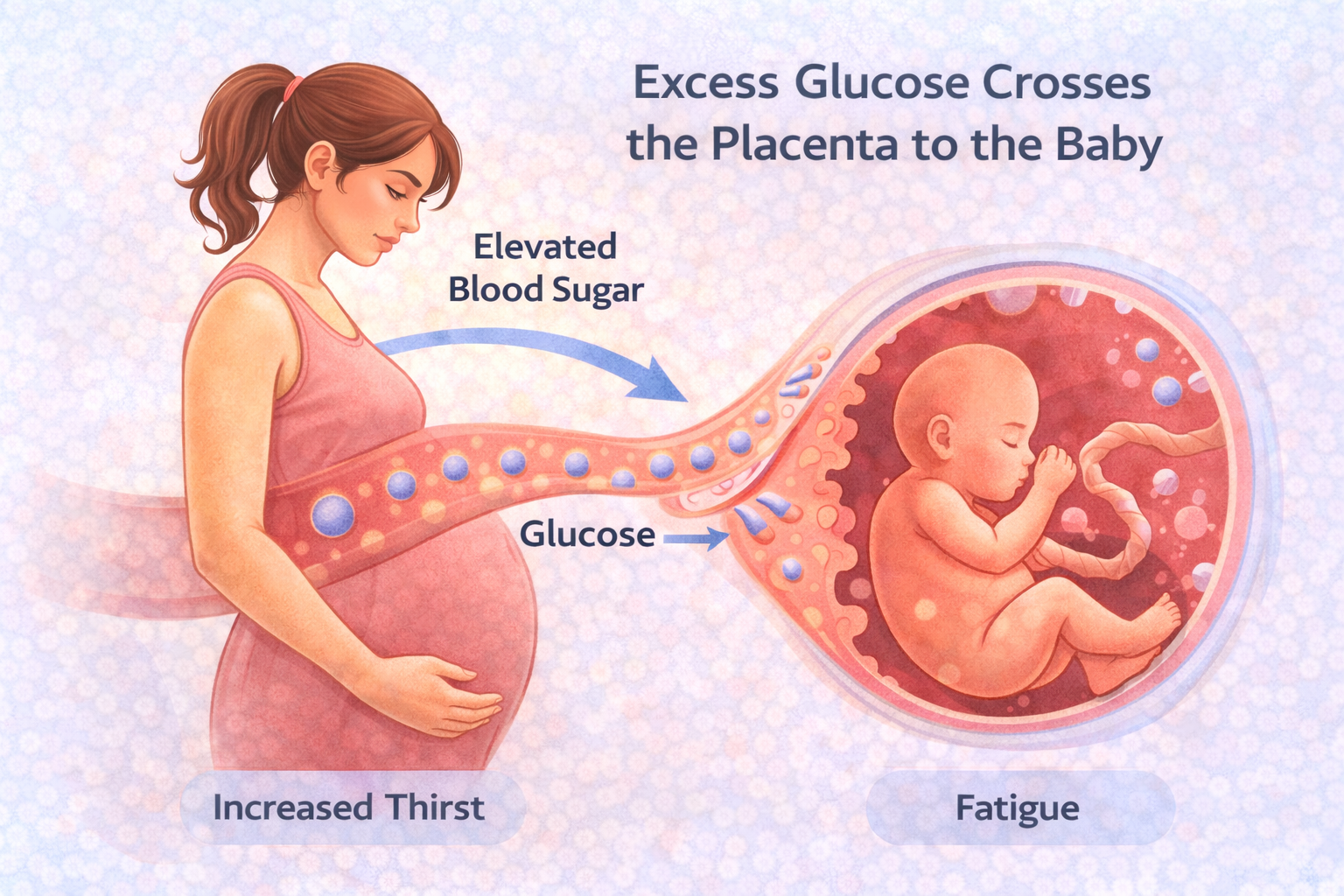
One of the most common effects of poorly controlled gestational diabetes is macrosomia, or excessive birth weight. Babies exposed to high glucose levels may grow larger than average, which can make delivery more challenging and increase the likelihood of birth injuries or cesarean delivery. This risk highlights why monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy is so important.
Another concern is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in the newborn shortly after birth. Babies who produce extra insulin in the womb may experience a sudden drop in blood sugar once the glucose supply from the mother stops after delivery. Doctors monitor newborns closely to manage this condition promptly.
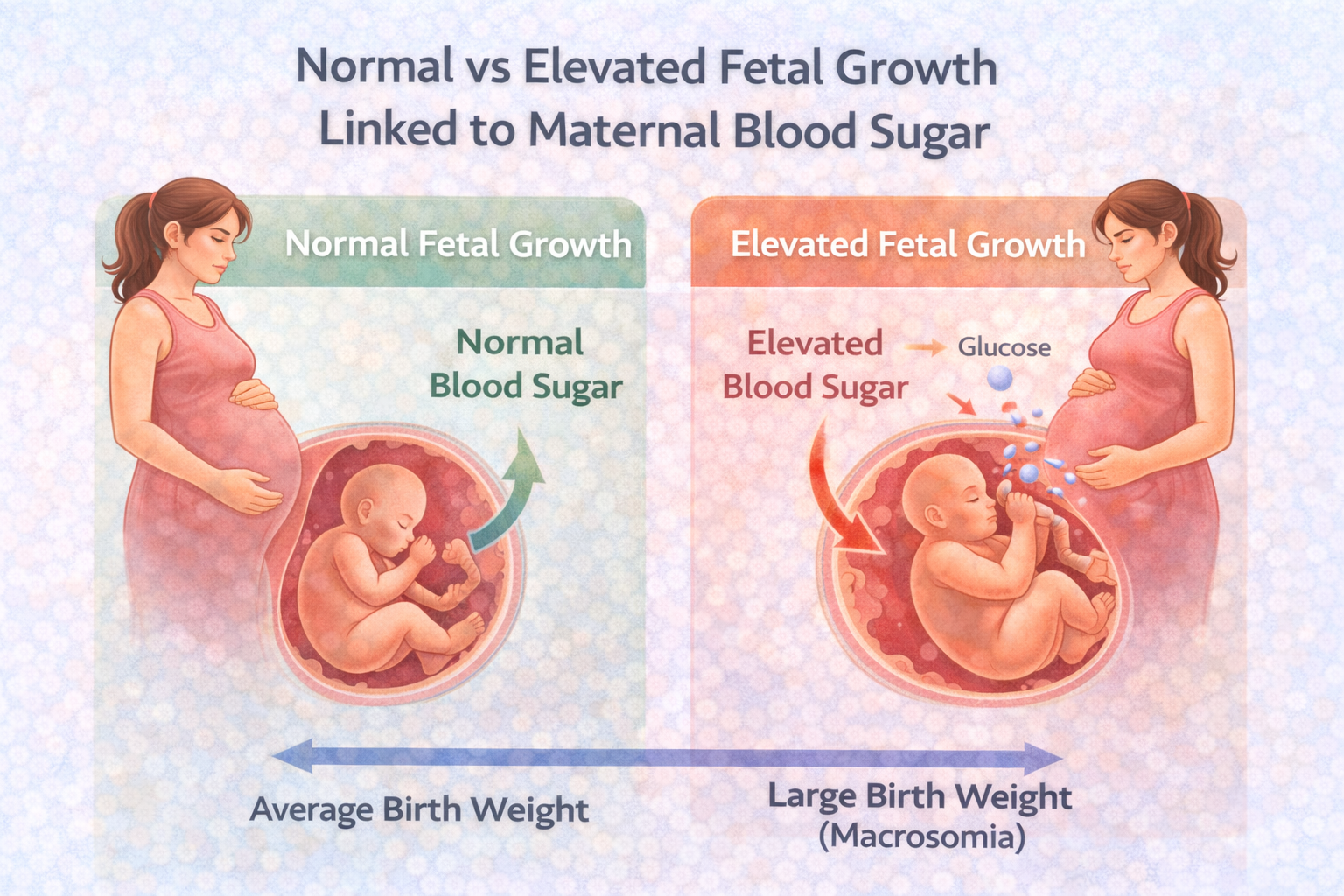
Gestational diabetes may also slightly increase the risk of breathing difficulties in newborns, especially if the baby is born early. Additionally, babies exposed to uncontrolled diabetes in pregnancy may have a higher likelihood of developing obesity or type 2 diabetes later in life. However, these risks are significantly reduced when blood sugar is well controlled during pregnancy.
It’s important to note that pregnancy diabetes symptoms in the mother are often mild or absent, which is why regular screening is essential. Many women search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to ensure timely diagnosis. Early detection allows doctors to guide mothers on diet, activity, and treatment to keep glucose levels within the safe range.
Working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy plays a key role in protecting the baby’s health. A specialist helps monitor glucose trends, recommends nutritional changes, and prescribes medication or insulin if needed. With proper management, most women with gestational diabetes deliver healthy babies without complications.

The reassuring news is that gestational diabetes does not automatically mean harm to the baby. When managed correctly, outcomes are usually very positive. Regular prenatal visits, glucose monitoring, and adherence to medical advice help maintain the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, reducing risks significantly.
Gestational diabetes can affect the baby if left unmanaged, but early diagnosis and proper care make a big difference. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing the importance of monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy help ensure the baby’s healthy growth and safe delivery. With the right care, most mothers with gestational diabetes go on to have healthy pregnancies and thriving babies.
Health Risks of Diabetes for the Mother
When a woman develops diabetes during pregnancy, the focus is often on the baby—but it is equally important to understand how diabetes in pregnancy can affect the mother’s health. While gestational diabetes is usually temporary, unmanaged blood sugar in pregnancy can increase the risk of several short-term and long-term complications for the mother.
Many women ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes? Pregnancy-related hormonal changes can reduce insulin effectiveness, causing blood sugar levels to rise. When glucose levels exceed the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, the mother’s body is placed under additional metabolic stress, which can lead to health concerns if not managed properly.
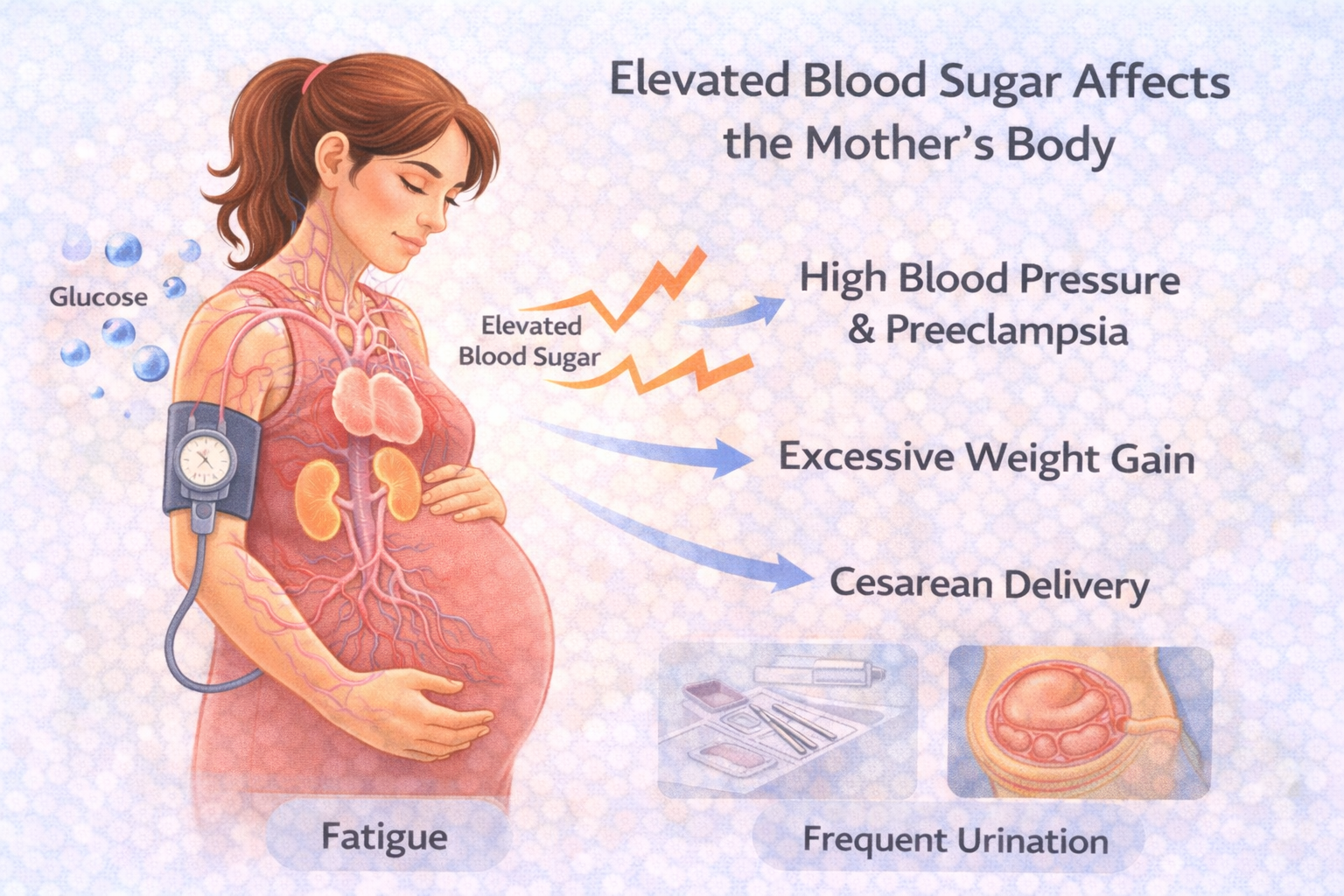
One of the most immediate risks is high blood pressure and preeclampsia. Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop pregnancy-induced hypertension, a condition that can affect the kidneys, liver, and overall circulation. This risk increases when blood sugar in pregnancy remains consistently high.
Another common issue is excessive weight gain. Elevated glucose levels can cause increased fat storage, making weight management more difficult during pregnancy. This not only affects maternal comfort but also increases the likelihood of delivery complications and longer recovery times after childbirth.
Pregnancy diabetes symptoms such as extreme fatigue, frequent urination, and increased thirst may worsen if blood sugar levels are not controlled. Persistent fatigue can make daily activities challenging and affect overall quality of life during pregnancy.

Women with diabetes in pregnancy also have a higher chance of requiring a cesarean delivery (C-section). Larger baby size and pregnancy complications often lead doctors to recommend surgical delivery, which carries a longer recovery period and increased risk of infection.
Another important concern is the risk of recurring gestational diabetes in future pregnancies. Women who experience diabetes during one pregnancy are significantly more likely to develop it again. Additionally, they face a higher lifetime risk of developing type 2 diabetes, making long-term health monitoring essential.
This is why early diagnosis is so important. Routine screening helps detect elevated blood sugar levels before complications arise. Many women search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule timely testing as part of their prenatal care. Early detection allows doctors to help mothers keep glucose levels within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
Working closely with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy plays a key role in protecting maternal health. Specialists help design personalized care plans that include dietary guidance, physical activity recommendations, blood sugar monitoring, and medication if required. With proper care, most women successfully manage diabetes in pregnancy without serious complications.
While gestational diabetes is common and manageable, it does pose health risks for the mother if left untreated. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, undergoing regular pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy are essential steps to reduce complications. With early diagnosis and proper management, most mothers experience healthy pregnancies and recover well after delivery.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Managed During Pregnancy?
Managing gestational diabetes during pregnancy focuses on keeping blood sugar levels within a safe range to protect both the mother and the baby. Although many women worry and ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes?, the good news is that diabetes in pregnancy can be effectively managed with the right medical guidance and lifestyle adjustments.
The primary goal of treatment is to maintain blood sugar in pregnancy within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. This is usually achieved through a combination of regular monitoring, dietary changes, physical activity, and medical care. Most women are able to manage gestational diabetes successfully without complications when they follow their care plan consistently.
One of the first steps in management is blood sugar monitoring. Pregnant women are often advised to check their glucose levels at home using a glucometer. Regular monitoring helps identify patterns and ensures that blood sugar remains stable throughout the day. This is particularly important because pregnancy diabetes symptoms may be mild or absent, making self-monitoring essential.
Diet plays a central role in managing diabetes during pregnancy. Doctors and dietitians help create a balanced meal plan that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods. Eating smaller, frequent meals helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar in pregnancy. Avoiding sugary foods and refined carbohydrates is key to staying within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
Physical activity is another important component. Light to moderate exercise, such as walking or prenatal yoga, helps the body use insulin more effectively. Exercise improves glucose metabolism and supports overall health during pregnancy. However, all activity should be approved by the healthcare provider.
Regular medical follow-ups are essential for effective management. Many women search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to ensure timely testing and follow-up assessments. These tests help doctors track progress and adjust treatment plans if needed.
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to control blood sugar levels. When this happens, medication or insulin therapy may be recommended. Consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures that treatment is safe for both mother and baby. Specialists carefully select medications and dosages to manage blood sugar without harming fetal development.
Education and emotional support also play an important role in management. Understanding how food, activity, and stress affect glucose levels empowers women to take control of their health. Healthcare teams provide guidance, reassurance, and continuous monitoring throughout pregnancy.
It’s also important to remember that gestational diabetes is usually temporary. After delivery, blood sugar in pregnancy often returns to normal levels. However, follow-up testing is recommended to ensure long-term health and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Managing gestational diabetes during pregnancy involves regular monitoring, healthy eating, physical activity, and professional medical care. By understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, maintaining blood sugar in pregnancy within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy, most women can manage gestational diabetes successfully and enjoy a healthy pregnancy and safe delivery.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips to Control Blood Sugar during Pregnancy
Managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy is essential for the health of both mother and baby. While many women ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes?, the reassuring fact is that diabetes in pregnancy can often be controlled effectively through the right diet and lifestyle choices. Simple daily habits play a powerful role in keeping blood sugar in pregnancy within a healthy range.
A balanced diet is the foundation of blood sugar control. Pregnant women should focus on eating small, frequent meals instead of large portions. This helps prevent sudden spikes and drops in glucose levels and keeps pregnancy sugar levels normal range throughout the day. Meals should include complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, combined with lean proteins and healthy fats.

Avoiding refined sugars and processed foods is equally important. Sugary snacks, desserts, and sweetened beverages can quickly raise blood sugar in pregnancy, making glucose control difficult. Choosing fiber-rich foods helps slow sugar absorption and supports steady energy levels.
Physical activity is another key lifestyle factor. Gentle exercises like walking, prenatal yoga, or stretching improve insulin sensitivity and help the body regulate glucose more efficiently. Even a 20–30 minute walk after meals can significantly improve blood sugar in pregnancy. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any exercise routine.

Hydration also plays a supportive role. Drinking enough water helps the body process glucose and maintain overall metabolic balance. Although diet and exercise are central, lifestyle habits like adequate sleep and stress management should not be overlooked. Poor sleep and high stress can disrupt hormone balance and worsen pregnancy diabetes symptoms such as fatigue and irritability.
Regular monitoring is essential, even when symptoms are mild or absent. Many women look for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to ensure timely testing and follow-up. Monitoring helps confirm that diet and lifestyle changes are effective and allows early intervention if sugar levels rise.
Working closely with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures personalized care. Specialists may recommend nutritional counseling, glucose monitoring schedules, and adjustments based on individual needs. With expert guidance, most women can successfully manage gestational diabetes without medication.
It’s also important to recognize that controlling blood sugar is not about restriction—it’s about nourishment. A healthy diet supports fetal growth while protecting the mother’s metabolic health. Maintaining stable glucose levels reduces complications and improves pregnancy outcomes.
Managing blood sugar during pregnancy involves smart dietary choices, regular physical activity, hydration, and consistent monitoring. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, maintaining blood sugar in pregnancy within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy can help ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy. With the right lifestyle habits, most women can confidently manage gestational diabetes and support their baby’s healthy development.
Does Gestational Diabetes Go Away After Delivery?
One of the most common concerns among women diagnosed with gestational diabetes is whether the condition continues after childbirth. Since diabetes in pregnancy is closely linked to hormonal changes, many mothers wonder what happens to their blood sugar levels once the baby is born. The reassuring news is that, in most cases, gestational diabetes does go away after delivery.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes from the placenta interfere with insulin function, leading many women to ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes? These hormones increase insulin resistance, causing blood sugar in pregnancy to rise above the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. After delivery, once the placenta is expelled, hormone levels drop rapidly. This allows insulin to work more effectively again, and blood sugar levels often return to normal within days or weeks.
For most women, pregnancy diabetes symptoms such as fatigue, excessive thirst, or frequent urination gradually resolve after childbirth. Doctors usually check blood sugar levels shortly after delivery to confirm that glucose levels are stabilizing. In many cases, no further treatment is required once blood sugar normalizes.
However, follow-up care is extremely important. Women who have had gestational diabetes are advised to undergo a glucose test about 6 to 12 weeks after delivery. Many mothers search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me even after childbirth to ensure proper monitoring. These tests help confirm whether blood sugar levels have returned to the normal range or if further medical attention is needed.
While gestational diabetes often resolves, it does increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Studies show that women who experience diabetes in pregnancy have a higher likelihood of developing diabetes again in future pregnancies or later adulthood. This makes long-term lifestyle care and periodic blood sugar monitoring essential.
Working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy doesn’t end at delivery. Postpartum guidance often includes advice on maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, and achieving a healthy body weight. These steps help reduce the risk of future diabetes and support overall well-being.
Breastfeeding also plays a positive role in postpartum blood sugar regulation. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and supports metabolic health, which can further reduce the risk of long-term diabetes. Many healthcare providers encourage breastfeeding as part of post-pregnancy care for women who had gestational diabetes.
It’s also important for women to be aware of early warning signs after pregnancy. If symptoms such as unusual fatigue, frequent urination, or unexplained weight changes return, it may indicate ongoing blood sugar imbalance. In such cases, prompt medical evaluation is advised.
Gestational diabetes usually goes away after delivery as pregnancy hormones decrease and insulin function improves. While blood sugar in pregnancy often returns to normal, women who experienced gestational diabetes should remain proactive about their health. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing pregnancy diabetes symptoms, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and continuing care with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy can help ensure long-term health. With proper follow-up and lifestyle choices, most women go on to lead healthy, diabetes-free lives after pregnancy.
Can Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented?
Gestational diabetes is a common concern among expectant mothers, especially those wondering, can pregnancy cause diabetes? While pregnancy-related hormonal changes are unavoidable, there are steps women can take to reduce the risk of developing diabetes in pregnancy. Although gestational diabetes cannot always be completely prevented, healthy lifestyle choices before and during pregnancy can significantly lower the chances.
One of the most effective preventive measures is maintaining a healthy body weight before pregnancy. Excess body fat increases insulin resistance, which can raise blood sugar in pregnancy. Women who enter pregnancy at a healthy weight are less likely to experience glucose levels rising beyond the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a critical role in prevention. Eating whole grains, vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps regulate glucose levels. Limiting sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and processed snacks reduces sudden blood sugar spikes. These dietary habits support stable blood sugar in pregnancy and lower the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes.
Regular physical activity is another important preventive strategy. Gentle exercises such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga improve insulin sensitivity and help the body use glucose more efficiently. Even moderate activity can reduce the risk of elevated blood sugar levels and minimize pregnancy diabetes symptoms like fatigue and excessive thirst.
Early and regular prenatal care is essential. Routine checkups allow doctors to monitor weight gain, blood pressure, and glucose levels throughout pregnancy. Many women search online for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to ensure timely screening. Early testing helps identify blood sugar changes before they develop into gestational diabetes, especially in women with higher risk factors.
Managing stress and getting adequate sleep are often overlooked but important preventive factors. High stress levels and poor sleep can affect hormone balance and worsen insulin resistance. Establishing healthy sleep routines and practicing relaxation techniques can support metabolic health during pregnancy.
Despite all preventive efforts, it’s important to understand that gestational diabetes can still occur in women with no obvious risk factors. This is because pregnancy hormones alone can sometimes overwhelm the body’s insulin response. In such cases, early diagnosis and management become the key focus rather than prevention.
Consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy can help women understand their individual risk and take proactive steps. Specialists provide guidance on nutrition, activity, and monitoring plans tailored to each pregnancy. Women with a family history of diabetes or prior gestational diabetes benefit especially from early specialist care.
Even when gestational diabetes cannot be prevented, outcomes are usually very positive with proper care. Regular monitoring helps keep glucose levels within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range, protecting both mother and baby from complications.
While gestational diabetes cannot always be prevented, healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, attending regular prenatal checkups, and undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me all contribute to prevention. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing early pregnancy diabetes symptoms, and working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy help ensure a safer and healthier pregnancy journey.
When Should Pregnant Women Get Tested for Diabetes?
Testing for diabetes during pregnancy is a vital part of prenatal care, even for women who feel healthy and have no obvious symptoms. Since many expectant mothers ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes?, understanding the right time for testing helps ensure early diagnosis and effective management of diabetes in pregnancy.
Most pregnant women are routinely screened for gestational diabetes between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. This is the period when pregnancy hormones significantly increase insulin resistance, making it more likely for blood sugar in pregnancy to rise above the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. Screening during this window allows doctors to detect changes early before complications develop.
Women with certain risk factors may need testing earlier in pregnancy. These risk factors include obesity, a family history of diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a previous history of gestational diabetes, or having delivered a large baby in the past. In such cases, doctors may recommend testing during the first trimester to monitor blood sugar in pregnancy closely.
One challenge with gestational diabetes is that pregnancy diabetes symptoms are often mild or completely absent. Some women may experience fatigue, frequent urination, or increased thirst, but these symptoms can easily be mistaken for normal pregnancy changes. Because symptoms are unreliable, testing plays a crucial role in diagnosis rather than symptom observation alone.
Many expectant mothers search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me as part of their prenatal planning. These tests are widely available at hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers and are simple, safe, and effective. The most common initial test is the glucose challenge test, followed by a confirmatory test if results are elevated.
Regular prenatal checkups also include ongoing monitoring of weight gain, blood pressure, and overall health. Doctors assess whether glucose levels remain within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range throughout pregnancy, especially in women with higher risk factors.
Consulting the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy is recommended if blood sugar levels are elevated or if there is a strong risk profile. A specialist provides personalized care, explains test results clearly, and outlines a management plan to protect both mother and baby.
Even after delivery, follow-up testing is advised. Women who experience diabetes in pregnancy have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Postpartum glucose testing helps ensure that blood sugar levels return to normal and supports long-term health.
Pregnant women should be tested for diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks, or earlier if risk factors are present. Since can pregnancy cause diabetes is a valid concern, timely testing is the best way to detect and manage the condition early. Understanding diabetes in pregnancy, recognizing possible pregnancy diabetes symptoms, monitoring blood sugar in pregnancy, undergoing timely pregnancy diabetes tests near me, and seeking care from the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy all contribute to a healthier pregnancy and safer delivery.
When to Consult a Doctor about Diabetes in Pregnancy?
Knowing when to consult a doctor about diabetes during pregnancy is crucial for protecting both maternal and fetal health. Many expectant mothers ask, can pregnancy cause diabetes? While gestational diabetes is common and often manageable, timely medical consultation ensures early diagnosis and prevents complications related to diabetes in pregnancy.
One of the earliest reasons to consult a doctor is if you experience unusual or persistent pregnancy diabetes symptoms. These may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, or recurrent infections. Although these symptoms can overlap with normal pregnancy changes, experiencing them consistently or intensely should prompt a medical evaluation to check blood sugar in pregnancy.
Women with known risk factors should consult a doctor early in pregnancy. Risk factors include obesity, a family history of diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or having had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy. In such cases, early testing helps monitor glucose levels and maintain them within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range from the beginning.
Routine prenatal visits also offer opportunities to assess the need for diabetes screening. Doctors usually recommend screening between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, but earlier testing may be advised if risk factors are present. Many women search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule timely screening as part of their prenatal care.
Consult a doctor immediately if routine test results show elevated blood sugar levels. Even if you feel well, high glucose readings indicate diabetes in pregnancy and require professional guidance. Early intervention helps reduce risks such as excessive fetal growth, delivery complications, and maternal health issues.
Working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy is especially important after diagnosis. Specialists provide tailored advice on nutrition, physical activity, glucose monitoring, and medication if needed. Regular follow-ups ensure blood sugar remains within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range throughout pregnancy.
You should also consult a doctor if you experience sudden changes such as rapid weight gain, swelling, high blood pressure, or decreased fetal movement. These signs may not always indicate diabetes, but they require medical assessment to rule out complications.
After delivery, follow-up care remains essential. Women who experienced diabetes in pregnancy should consult a doctor for postpartum glucose testing to confirm that blood sugar levels have returned to normal. Continued medical guidance reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes During Pregnancy
Is it normal for pregnant women to get diabetes?
Yes, it is more common than many people realize. Diabetes in pregnancy, often called gestational diabetes, occurs due to hormonal changes that affect how the body uses insulin. While not every pregnant woman develops it, the condition is considered common and manageable with proper care.
Can pregnancy cause diabetes even if I was healthy before?
A common question is, can pregnancy cause diabetes? Pregnancy itself does not cause permanent diabetes in most cases, but pregnancy hormones can temporarily reduce insulin effectiveness. This leads to increased blood sugar in pregnancy, even in women who never had diabetes before.
What are the symptoms of diabetes during pregnancy?
Pregnancy diabetes symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, or recurrent infections. However, many women experience no noticeable symptoms at all, which is why routine testing is so important.
What are normal blood sugar levels during pregnancy?
Doctors monitor glucose levels to ensure they stay within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range. These ranges are slightly different from non-pregnant values and are designed to protect both mother and baby. If readings consistently exceed this range, further evaluation is required.
How is diabetes in pregnancy diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through routine blood tests, usually between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Many women search for pregnancy diabetes tests near me to schedule screening as part of their prenatal care. Testing is simple, safe, and essential for early detection.
Does gestational diabetes affect the baby?
If unmanaged, elevated blood sugar in pregnancy can affect the baby’s growth and delivery. However, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, most women deliver healthy babies without complications.
How is diabetes during pregnancy managed?
Management usually includes dietary changes, physical activity, regular blood sugar monitoring, and medical supervision. Some women may need medication or insulin. Working with the best diabetes doctor for pregnancy ensures personalized care and safe glucose control.
Will gestational diabetes go away after delivery?
In most cases, yes. Blood sugar levels usually return to normal after childbirth. However, women who experience diabetes in pregnancy have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, so follow-up testing is recommended.
Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
While it cannot always be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, staying active, and attending regular prenatal visits can reduce the risk. Early screening helps catch changes before complications arise.
When should I consult a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if you have risk factors, experience persistent pregnancy diabetes symptoms, or receive abnormal test results. Early consultation helps keep blood sugar in pregnancy within the pregnancy sugar levels normal range.